Clinical Trial Mythbusters
Clinical Trial MythBusters: What Is the Value of Diversity in Clinical Trials? from Patient Empowerment Network on Vimeo.
Downloadable Program Guide
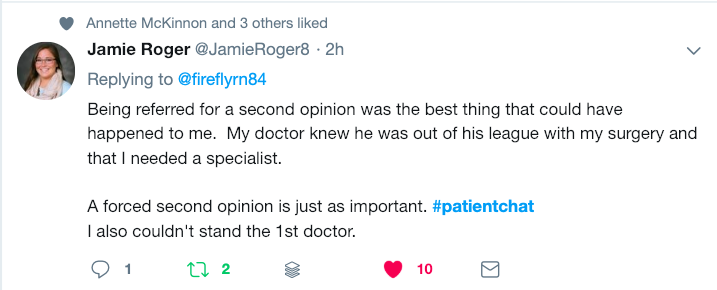
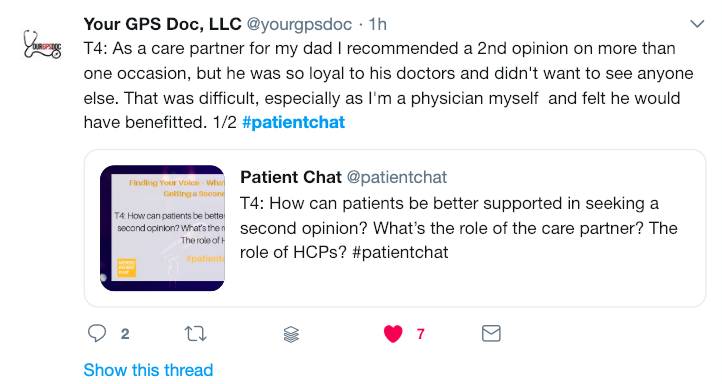
In this MythBusters program, Senior Vice President and Chief Medical Officer (CMO) of ASCO, Dr. Robert Schilsky, and 20+ year CML survivor, Mel Mann along with Cecelia Mann, will unpack some of the issues that have led to the lack of diversity in clinical trials and initiatives in place that are changing all of this.
Transcript:
Andrew Schorr:
And greetings from near San Diego, Carlsbad, California. I’m Andrew Schorr from Patient Power. Welcome to this Patient Empowerment Network program, the next in our series Clinical Trial Mythbusters, and this program is so important, discussing what is the value of diversity in clinical trials. And, believe me, you’ll hear it is so critical. We have to do better, and we’re going to discuss that over the next hour.
I want to thank the companies that have provided educational support through grants to the Patient Empowerment Network. They have no editorial control, but their support is welcome. And that is AbbVie Incorporated, Astellas, Celgene and Novartis. All right.
We’ve got a lot to discuss today, and we welcome your questions along the way. I want to first introduce someone who, like me, has greatly benefited from a clinical trial and believes that they are alive today because of their participation. And so joining us from Atlanta is Mel Mann along with his wife and care partner Cecelia Mann. Mel, welcome to the Patient Empowerment Network program.
Mel Mann:
Thank you very much.
Andrew Schorr:
And we’re going to hear more of Mel’s story in just a minute. I want to introduce a very prominent medical expert who joins us. He is the senior vice president and chief medical officer at really the largest cancer organization, the American Society of Clinical Oncology, and that is Dr. Richard Schilsky. Dr. Schilsky, welcome to our program.
Dr. Schilsky:
Thank you, Andrew. Happy to join you.
Andrew Schorr:
Okay. And are you in the Washington, DC, Virginia area?
Dr. Schilsky:
That’s where our organization is based, in Alexandria, Virginia, yes.
Andrew Schorr:
Thank you for being with us. I should mention that Dr. Schilsky has had a lot of experience related to trials. He was the head of hematology/oncology at the University of Chicago, which of course Chicago is a very diverse city, and the University of Chicago does a lot of research. And he also helped run a big research group that doctors from around the world are part of, and he did that for many years. So we’re going hear more from Dr. Schilsky in just a minute. But, first, Mel. So Mel, in the late ’90s you were dying, right, of chronic myeloid leukemia, correct?
Mel Mann:
Yes, I was.
Andrew Schorr:
Losing weight and being told that there wasn’t much to do, right?
Mel Mann:
Correct, yes.
Andrew Schorr:
Maybe a transplant. But you were in Atlanta and you went from doctor to doctor, but somehow you got to MD Anderson, a major research center in Houston. What did they offer you there?
Mel Mann:
When I first went out to MD Anderson they said they were going to put me on a clinical trial after clinical trial. And the first thing they did was increase my dose of interferon, and that was the medication, the standard therapy at the time, and then they tried different combinations of drugs, and eventually I started on different clinical trials.
Andrew Schorr:
Okay. And, Cecelia, you were there in Atlanta and he was scooting over to Houston, it’s not exactly around the corner. Why were you supportive of that?
Cecelia Mann:
I was supportive of that because that was the last chance that he had to a cure and for survival. So from the very beginning, whatever type of treatment he needed when he was flying around, whether he was going looking for bone marrow transplants, doing bone marrow drives, and therefore I was supportive of. We had a five‑year‑old daughter at the time, and so anything that Mel needed I was there to support him.
Andrew Schorr:
So, Mel, this is a happy story because here we are in 2018 as we do this program and you are with us when many people with CML at the time were not with us that long. Hopefully, a transplant could be curative, but a lot of people passed away. You were lucky enough to come back as they were rolling through different trials and there was a new one that opened up for a drug called Gleevec, a pill.
Mel Mann:
Yes.
Andrew Schorr:
What happened?
Mel Mann:
Okay. So in the summer of ’98 the Phase 1 Gleevec study opened up, and I went out to MD Anderson, and I was patient number two, and I started taking it at a low dose, and it was effective for me. And eventually they increased the dose and it started changing my leukemia around to eventually I reached what they call a major molecular response. And that was 20 years ago. This summer I went over 20 years.
Andrew Schorr:
Wow. Well, Dr. Schilsky, is that an example of a patient getting, if you will, tomorrow’s medicine today, what we hope for?
Dr. Schilsky:
Absolutely. And, first of all, it’s such a wonderful story, Mel. It’s great to hear you tell it, and it’s exactly why we do research, exactly why we do clinical trials, to try to discover the new therapies that people need that will give them the kind of long‑term survival and quality of life that you’ve been experiencing. It’s just‑‑it’s wonderful.
Andrew Schorr:
So, Dr. Schilsky, let’s get into the problem. So, generally, there are many clinical trials that take longer than one would hope to fill, and the FDA and I know scientists have been seeing well, gee, how do we know what we’re testing applies to people maybe with different ethnic, gender backgrounds, a variety of situations, and often we can’t find people who fit those categories to be in. What is that‑‑how poorly have we been doing in the past with diversity in trials, and what does that mean for developing new medicines?
Dr. Schilsky:
Well, we don’t do well in almost any dimension. We don’t get enough underrepresented minorities in clinical trials. We don’t get enough older people in clinical trials. You have to remember that 60 percent of cancers occur in people 65 years and older, and yet only about 10 percent of people participating in clinical trials are 65 and older. So we are having to treat the majority of older people, and I would say the majority of minority people, with data derived from participants in clinical trials who are not like them.
We need to change that for a whole host of reasons. It’s historically been very challenging, and the problems really sort of boil down into three big areas that I think we can discuss a little bit further.
First is awareness. Many people are not aware that clinical trials are even an option for them. Many people think that a clinical trial is a last resort, and I want to dispel that myth right out of the box. Clinical trials can be a very good option for patients right from the time of their cancer diagnosis even if it’s their very first treatment. So clinical trials may be a last resort, but they don’t have to be, and there are many clinical trials that are appropriate for people right following the initial diagnosis of their cancer.
So there’s the awareness issue, and sometimes, frankly, not even the doctors are aware of what clinical trial options are for their patients. And the one thing we know for sure is that the most influential person as to whether or not a patient goes into a clinical trial is their doctor. If the doctor does not recommend it, if the doctor is not aware of it, it’s not going to happen.
But then you get into the more technical issues. There are things, there are rules for clinical trials because they are research studies. They are experiments. There are very well defined rules, most of which are in place to protect the people who are participating in the study. Some of these rules are called eligibility criteria, and they specify the characteristics of people who can enroll in the study. Well, historically, they tend to be very rigid and very limiting, and you’ll often hear people talk about how the only people who can get into clinical trials are Olympic athletes. That may be the case, but it’s not Olympic athletes that we’re treating in the clinic every day, so we need to make our clinical trials more representative so that they’re more applicable to the typical person that a doctor sees in their office.
And then there are the logistical or operational issues of the clinical trial. The clinical trial can be very burdensome. Mel just described how he had to travel from his home in Atlanta to Houston to participate in a clinical trial. Not everybody can afford to do that. Not everybody can take time away from work, time away from home. And the clinical trial requires not only that you travel sometimes but that you travel on a specific schedule because of the requirements of the trial.
So all of these are issues that are‑‑can limit participation in trials, and many of them are magnified in minority populations or in populations that don’t have the economic resources to be able to meet the requirements of the trial.
Andrew Schorr:
Right. Let’s talk about that for a minute. So, Cecelia, you go out in the community and speak to people, and you probably meet some people who maybe are diagnosed with a blood cancer, like you’re active with the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society so you may speak to them, and they say even if you brought up about a trial, they say, hey, Cecelia, I’m working two jobs. Or my husband or spouse is working two jobs, and we’ve got two kids, three kids. How could we ever participate? We just can’t get away or we don’t have the family support or whatever. Those are real issues, right?
Cecelia Mann:
True. True, those are real issues, and I try to direct them towards resources that Mel and I found out about along the way. The Leukemia and Lymphoma Society, they have resources to help with travel, and American Cancer Society has resources that help with the hotel and lodging. And there are a number of other different types of funds that can be assessed to make that a possibility.
But you’re right, Andrew. I had one young lady at a health fair and a second cancer had popped up, and she was coming there to get information, and she was saying that they were saying it wasn’t too much they could do, and I brought up MD Anderson. And she immediately said, I can’t go out there, I have to go to work, and she turned around rough. And so when they listen to me then always glad to tell them about it and let them know there is an option and that clinical trials work, and I point to Mel, my husband, as a success story also.
Andrew Schorr:
So, Dr. Schilsky, you talked about physician awareness. It’s also about more physicians participating in trials at I think what you call the community level. So, in other words, MD Anderson and where you work, at the University of Chicago, those are big city centers and where they are in Atlanta there’s Emory and some other mainly centers, but what about out in the hinterland, if you will? Can somebody who lives there diagnosed with a cancer, how do they have access to a trial that their doctor knows about and maybe that’s more close to home, if you will?
Dr. Schilsky:
Right. So of course we know that anybody with cancer prefers to be treated in their community, and most are. So one of the goals is to be sure that oncologists practicing in all sorts of community settings have access to clinical trials. Now, one of the ways that happens is that for more than 50 years now the National Cancer Institute has actually been operating and funding a community‑based clinical trials network. It used to be called the CCOP program. That’s an acronym that we don’t have to go into. They’ve recently changed the name. It’s now called NCORP program, but‑‑that stands for, I think, the National Community Oncology Research Program.
But the point is that the program, which is in most but not all of the states in the United States, funds community oncologists to participate in NCI‑sponsored clinical trials, and there are at least 65 or 70 such clinical facilities around the country right now. So in those medical practices patients can find those clinical trials in their communities without having to travel.
There are also other community‑based networks that are active participants in cancer clinical trials. So I think at the end of the day the critical thing for patients, and this is sometimes easily forgotten because you’re so, you know, your thinking and your time and your emotion are all taken up in dealing with the cancer diagnosis. It’s really important, though, to ask the doctor, do they have access to clinical trials. Do they have a clinical trial that might be appropriate for you? And if not you might want to consider where else you could go, hopefully still relatively nearby to get access to a clinical trial.
Andrew Schorr:
Mel, so for you, you went around to some doctors who were not aware of anything new to do for you, right? And that’s still true in so many areas of cancer. Now, what do you say to patients about speaking up because Dr. Schilsky just referred to it, people are terrified. They really just want the doctor to have the answer. What do you tell people so that they maybe advocate for themselves?
Mel Mann:
Okay. So if you’re looking for a clinical trial and I’m out at, like you say, a health fair, we have a‑‑the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society has something called the clinical trial support center, and they have nurses who work early in the morning till late at night. And you call them up and you tell them about your illness, and they check the availability for what clinical trials are out there, and then they narrow it down to what you actually qualify for, and then they take into consideration your finances and other issues.
And then you’re left with a number of possible clinical trials that you have, and you can take that back to the doctor and you can discuss that with him. So that’s one of the things I talk with them about.
Andrew Schorr:
I could mention, now this is really more broadly across cancer, too. So there are breast cancer groups, there are lung cancer groups, and I would just make a pitch to find out, is there a local chapter or national number for you, for the cancer you or a loved one been diagnosed with, and that’s the question.
Mel Mann:
Yes.
Andrew Schorr:
Say, look, A, I don’t want to feel I’m alone, and, B, how do I get‑‑how do I get connected with what could be lifesaving or life‑extending treatments for me and that I could discuss with my doctor. And understanding‑‑and then, boy, if there are obstacles like financial issues, logistical issues, travel issue, is there support for that.
Mel Mann:
Yes.
Andrew Schorr:
So let’s go back to the inclusion/exclusion or eligibility issue you spoke about, Dr. Schilsky, because, you know, somebody who has cancer may also have heart problems or diabetes or some other issue. Maybe they previously had another cancer, and so for the companies developing new drugs they may be happy with narrow inclusion criteria because they don’t want to have anything get in the way, some previous thing you’ve had, to affect their ability to have a new drug go on the market.
So what kind of work is going on between government and the drug manufacturers so that the criteria, not so tight, but you can still get legitimate scientific answers?
Dr. Schilsky:
Right. So, as you alluded to, Andrew, there are good reasons that there are eligibility criteria. One of them is to protect the patients in the study from circumstances that would increase their risk of participating in the study. Another is because the companies or whoever is sponsoring the study wants to be able to isolate the specific effect of what they’re studying without having a lot of confounding factors that could muddy the water and makes it difficult to interpret the results. But that said, the bad thing about all that is that the results of the study might not be applicable to the majority of people who could benefit from the treatment because they weren’t included in the study to begin with.
So one of the things that my organizations has been working on very hard over the last couple of years now, and we’ve been doing this collaboratively with people from the Food and Drug Administration and the National Cancer Institute and a lot of clinical experts and a patient advocacy group, Friends of Cancer Research, is to try to expand or broaden or simplify some of these eligibility criteria that tend to keep people off of trials and in particular tend to keep minority populations off of clinical trials.
So, for example, it’s not unusual for someone who has a new diagnosis of cancer to have previously had some kind of cancer earlier in their lives. So we might see a patient who has lung cancer who 15 years ago had a diagnosis of prostate cancer. Well, for that lung cancer patient to go on a trial that has the typical inclusion and exclusion criteria that doesn’t allow for this previous malignancy, they would be excluded even if they had been cured of that prostate cancer 15 years ago.
We also see, and you mention what we call in the medical profession comorbidity. So if someone’s got cancer and they also have heart disease, they also have diabetes, high blood pressure, anything that affects the functioning of your normal organs, can also exclude people from participating in trials, and there are certain limits that we feel can be expanded and still allow the treatment to be given safely.
So just about a year ago now we came out with a set of recommendations for how eligibility criteria can be modified to make clinical trials more inclusive. And now just recently, I’m really pleased to say, the National Cancer Institute expanded their sort of template protocol document that many investigators follow to incorporate our recommendations, so now their standard protocol includes these broader inclusion and exclusion criteria. And the FDA now is working on what they call guidance documents to advise commercial companies that are running clinical trials to do just the same thing. So we are very optimistic now that we’ve got this ball rolling. We’re going to be removing these obstacles, and we’re going to be able to have more inclusive and diverse population of patients who participate in cancer clinical trials.
Andrew Schorr:
Great leadership. I hope it works great, and we’ll be happy to support you. So, Mel and Cecelia, let’s talk about the money part of it a little bit. So you were making trips to Houston, Mel, Cecelia was home with a five‑year‑old, and so admittedly there may be hardships, financial hardships, being away from family if you have to go to a trial somewhere else, checking back. What do you say to people when they say, well, I’m just going to go with the traditional stuff. It’s close to home. In other words, if there can be programs that can help them it still takes courage, if you will. So what would you say to people about investing in their life, if you will?
Mel Mann:
Well, you know what the standard, what the current treatment is and the outcome of that, so if you want to have a different outcome then you have to try something new which is probably going to be a new drug. So you have to weigh that with the cost and the travel. Some people may not have the support, the caregiver support to go a long distance, so you have to take that into consideration. As far as the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society they do have certain funds where they can help with travel pay, co‑pay, insurance premiums, that could help alleviate some of it. So there’s a lot of stuff that’s involved, and it’s an individual decision.
Andrew Schorr:
So we’ll just make a comment, though. So, many people have a church or synagogue, friends, neighbors even if they’re living alone, but yet people are sometimes hesitant to ask for help. And I would say speak up. People do want to help you.
Dr. Schilsky, let’s talk about another reality of trials. There’s a history certainly and some fear still in the black community of whether they were tested on, without their knowledge even, going back years and the general thought, you’ve heard it through your career, I’m sure, people say, well, I don’t want to be a guinea pig for a couple reasons. One is we don’t know if it’s going to work. And second of all if there are different arms of a trial I don’t know if I’m going‑‑I’m going to go to all this trouble and expense, I don’t know if I’m going to get the good stuff. So maybe you could speak about that a little bit. First of all, the fears of being experimented on, and then also about whether you will get what could be a breakthrough.
Dr. Schilsky:
Yeah. Well, for sure, you know, there is this sort of sordid history of inappropriate experimentation on people, and clinical trials are a form of experimentation. They are a form of research. There’s no doubt about that. But clinical trials these days are highly regulated, overseen by independent groups that include patients and clinical experts that come together in committees called IRBs, Institutional Review Boards, and they evaluate on both the risks and the benefits to patients who participate in clinical trials.
They make sure that the trial has an appropriate consent process associated with it, that it’s explained in plain language to patients, so I think these days a lot of those concerns no longer exist. And I hope that people can get beyond the history that led to some of those concerns. The‑‑sorry, I lost a train of thought on the rest of your question.
Andrew Schorr:
The issue about are you going to get the good stuff.
Dr. Schilsky:
Oh, yes. So a couple points there. One point I want to make clearly is that in most cases cancer clinical trials do not include a placebo or an inactive treatment. That’s not always the case, but it’s true most of the time. So patients are always going to get at least the standard of care treatment, and of course the standard of care is what is at that time known to be the best available treatment.
The whole point of doing the research is to determine if the new thing is better, and of course we always hope it will be. It’s not always better, but sometimes it is, as in Mel’s experience. And I think this has to be clearly laid out to patients. They have to clearly understand why the research is being done. In many trials nowadays even if the patient is assigned to get the standard of care treatment there still may be an option to get the new treatment at a later point. So if the standard of care doesn’t work many times there’s still the opportunity to get the new treatment following the standard of care treatment.
So the trial really boils down to not standard versus new but new versus standard followed by new. So eventually everybody may have a chance to get the new treatment. That’s not always the case, but I think the key‑‑my key take‑home, in a sense, is that we’re doing the research because we think and we hope the new treatment is better, but we have to do the research to prove that. And everybody in a clinical trial I think can be assured that they’re going to get, at the very least, the best available standard treatment.
Andrew Schorr:
Mel, when you signed the papers to be in a trial, and you probably shared them with Cecelia, especially back in the late ’90s and I participated in one trial in 2000 and another in 2011, there’s a lot of paperwork, things in bold face written by lawyers. I didn’t always understand it. What propelled you beyond that? Was it just that, oh, my god, if I don’t get something I’m going to die? Or how did you two deal with the paperwork and feel comfortable signing on the dotted line?
Mel Mann:
Well, I saw a lot of hope in the paperwork. For example, one trial I was on was peginterferon, and I had been taking interferon every day, injecting myself, and I had to keep it refrigerated and when I travelled it made it difficult. So with peg I can take one shot a week, so that would make the cancer journey easier. It may not make me live longer, but it will improve my quality of life, so I saw my quality of life improving with that clinical trial. And I looked at the paperwork, and I went through it, and I felt comfortable with it.
Andrew Schorr:
And how about you, Cecelia? I mean, your husband says, well, I’m going to be in a trial and I’ve got to sign all these papers. Did you say at any point, wait a minute, that’s scary?
Cecelia Mann:
Well, no, I didn’t. I didn’t because with Mel, he had three years to find a marrow match, and he was at the end of year two and no match in sight. And so when he had the opportunity to go out to MD Anderson and be on a clinical trial or several, I was okay with that. I was okay with that. And I looked at it as actually being a blessing. And it turned out to be, and we’re grateful.
But I would say to anyone else who is contemplating a trial and that person and their caregiver, their spouse, to just educate yourself, and get as much information as you can, ask as many questions as you can, but please don’t just throw it away out of hand. It’s definitely worth considering.
Andrew Schorr:
Dr. Schilsky, so we have more than 50 million people with a Hispanic background in the United States, and even if many people are speaking English they may speak Spanish at home. And then when you are diagnosed with a cancer there’s a whole new language of stuff that comes into play that even if you’re fluent in English it may not be either what you easily understand or even aligns‑‑what’s being asked of you aligns with your cultural background. Okay? So how, beyond, let’s say, the African‑American community, when you look at the Hispanic community, how do we encourage participation there and get over some of these cultural or language nuances, if you will?
Dr. Schilsky:
Yeah. So it’s much the same thing in the sense that the same information has to be conveyed but it may have different meaning and different interpretations in different ethnic and cultural groups. Most clinical trials now will have a consent form that is fully translated into Spanish. But, of course, there are many different languages on the globe. When I was practicing at the University of Chicago for many years on the south side of Chicago, we had Polish‑speaking people, we had Russian‑speaking people, we had people‑‑Chinese‑speaking people.
So the requirements actually are that there must be a consent form, at least some reversion of which is translated into the first language of the patient. So if you’re a native Spanish speaker, a native Chinese speaker, you have to have, be able to see a consent form written in that language, and generally speaking you have to have your native language interpreter present in the room to help you go through the consent form and respond to your questions. And that person has to be someone who is independent from the research team so they can give you the straight answer and not be influenced by any member of the research team. So I think all of that certainly helps.
But, again, what helps a lot more is to have members of the care team who look like the patient. So we have problems with diversity in our profession as well. We have very few African‑American oncologists. We have more Spanish‑speaking oncologists, but again we have few Asian oncologists. So we need to do a better job of improving the diversity of our profession, improving the diversity of the care teams. We need nursing staff and research staff and other people who work with our patients who represent them and gain their trust, who look like them, who talk their language. And I think that will go a long way toward making people feel more comfortable about participating in clinical trials.
Andrew Schorr:
I was at a conference last week and I heard some of the patient experience, people from different drug companies talking about how they were trying to simplify their forms because I know in 2000 when I entered a Phase 2 trial there were all kinds of black boxes, you could die, you could this, everything in the kitchen sink was in it. I’m still here, and I think because of the trial, and most of the side effects I didn’t have or they were definitely handled extremely well.
So right now, where are we, Dr. Schilsky, with participation? And why is it important? In other words, in this age of personalized medicine why do we need more black people in certain trials? Like, I know in multiple myeloma, one of the areas we cover, there’s a higher incidence in the black population, right, but yet few black people are in the trials for myeloma drugs. Or maybe there are differences with Asian populations or other populations. So is it that you can’t really get a clear scientific answer on the differences? Is that it?
Dr. Schilsky:
That’s part of it. First of all, we want anybody who could potentially benefit from being in a trial to be able to be in the trial for their own personal benefit. Secondly, we need to learn about the performance of the drug or the intervention in all the diverse populations in which it might be used. And one of the things we have learned is that not all populations respond the same way. Some treatments are more toxic in certain racial or ethnic groups. Some are more effective in some racial or ethnic groups.
And, you know, since you brought up this whole new world of precision medicine, I’ll give you the example of the lung cancer drugs that are used to treat the specific mutations in a gene called EGFR. So that’s a gene which has mutated in about 15 percent of Caucasian patients with lung cancer, but it’s mutated much more commonly in Asian patients. And in fact one of the clues that there was even a gene mutation that was important in determining whether these drugs worked or not was because it was observed that the drugs worked better in the Asian patients in the clinical trials even before the genetic abnormality had been discovered. And the clue was what’s different about the Asian patients than the other patients in the trial.
So the diversity is critical to our learning and critical to our application of the therapy in all the diverse populations that we serve.
Andrew Schorr:
If you’re in our viewing community and you have a question, send your questions into questions@patientpower.info, questions@patientpower.info. We’ll continue our discussion of course, but we invite you to join in.
So, Mel, when you get to talk to people, what do you say? Somebody is sick, diagnosed with a cancer, what do you say? Dr. Schilsky was talking about not seeing clinical trials as a last resort, and you weren’t seeing it that way (?) Inaudible, but today what would you say to people when you talk to them about it?
Mel Mann:
Well, I will say explore your possibilities because there are all different opportunities at each phase. You may not go into Phase 1 but you could do a Phase 2, 3, 4‑‑or Phase 3, and you don’t know what’s going to happen in each of those phases. So you just have to see what’s out there. And I’m exhibit A, so they look at me and they say, well, I can work, and then not as suspicious, you know. We have Tuskegee, and that was 1972, and it was that dark period of cancer history so that kind of rolls around in their mind, but you can’t let that jeopardize the opportunity such as Gleevec that I took advantage of. So we know that Gleevec worked, and there are other drugs that have improved the quality of life and the lifespan of cancer patients. So definitely research those drugs.
Andrew Schorr:
Did you lose heart when you were first in one trial and the medicine wasn’t working for very long? Some would say, well, all right, I tried a trial, forget about it, you know. But you then pursued other trials. What propelled you to do that?
Mel Mann:
Well, I was still in the game, so I saw that these trials took‑‑well, first of all, I could not find a bone marrow donor, but a bone marrow transplant was pretty drastic in itself so I was looking at these other opportunities as maybe not even having to take part in‑‑have a bone marrow transplant. So that was another incentive. So‑‑and I knew that if I didn’t find one‑‑there was a very small chance, there was only about 5 percent of Americas who are on the marrow registry, so basically I was helping to build a list, maybe not for myself but for people in the future who needed a transplant.
Andrew Schorr:
Dr. Schilsky, let’s talk about the pace of research. So, first of all, if we don’t get enough participation in trials how does that slow drug development?
Dr. Schilsky:
Well, it slows it down enormously because we have to have a certain number of people in each trial to be able to get a reliable answer. And these days it’s becoming even more challenging because as we’re developing drugs that only target a specific genetic abnormality in the tumor which sometimes is very rare so we may be looking for a genetic abnormality that only occurs in 2 or 3 percent of all people with a certain kind of cancer. First you have to find the people who have that genetic abnormalities, then you have to be able to enroll them in a clinical trial. They have to be willing. They have to meet the enrollment criteria. So it can take a long time, and even a global effort to find enough people to fill out a clinical trial.
And most clinical trials in order to produce a reliable result are going to require a minimum of 50 to 100 patients. Some require many hundreds of patients or even many thousands of patients depending on the question being asked. So you can see if people are not participating it’s going to take long time to get those answers.
Andrew Schorr:
Now, Mel, you got Gleevec in a trial at least three years before it was approved, and it was approved fast because it was such a breakthrough, right? So you literally got tomorrow’s medicine today, and it saved your life in the process, right?
Mel Mann:
Yes, because I was past the three years. I was about three years and eight months in my diagnosis, so you add another three years onto that and I would not have been here.
Andrew Schorr:
Right. In my case I was in a trial related to chronic lymphocytic leukemia, three‑drug combination, and I received that in a Phase 2 trial 10 years before that was approved. So it was a long time.
So I have a question for you about personalized medicine, Dr. Schilsky. So for instance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia I’m not‑‑I’m Caucasian but I’m Ashkenazic Jewish, okay? So where we’re going with personalized medicine, are we beginning to find subsets among Caucasians, among African‑Americans, among Asians, where there are even more narrow slices to help us understand targeting of medicines and what’s effective for whom? Is that where we’re headed?
Dr. Schilsky:
Absolutely. And, as I said earlier, we’re seeing that all the time. So almost every common cancer now is being broken down into a whole basketful of rare cancers under the broad umbrella of whatever the cancer type. So lung cancer, there’s probably six or eight different kinds of lung cancer now that each have a specific genetic abnormality, that each requires a specific treatment. And many of those treatments now are FDA approved, but the first thing you have to know is does the cancer have the genetic abnormality and then what is the appropriate treatment to use. We’re seeing that in breast cancer, in melanoma, in many other kinds of cancer types.
There’s another‑‑there’s a related issue here, though, of course, which is that not everybody metabolizes drugs the same way, and so another reason to have diverse populations in a clinical trial is to learn about side effect profile of the drug, learn about the right dose of the drug to use. And we know full well, for example, that African‑Americans metabolize some drugs differently from white people, and so, depending upon how the drug is working in the body, an African‑American person might require a higher dose or a lower dose of the same drug that a white person would require in order to get the same therapeutic effect.
So it just speaks to the point again where if you don’t have diverse populations in the trials you can’t learn this stuff so that doctors then have the information they need to be able to prescribe the drug in the best way for their particular patient.
Andrew Schorr:
Okay. Here’s some questions we’ve been getting in. Kaitlin wrote in, Mel, she wants to know, do you still participate in follow‑up activities related to the trial you were in? So tell us about your participation and sort of follow‑up.
Mel Mann:
My follow‑up is I go out to MD Anderson twice a year, and it’s just a one‑day, one‑hour doctor visit where they take the blood work and they check and see if everything’s stable. And then when I’m back home, twice a year I have my blood work checked back at home, and that’s the extent of the follow‑up. I still have to take medication, one pill a day.
Andrew Schorr:
Right. And is that still covered by the trial?
Mel Mann:
Well, it’s covered by the trial, but my insurance also covers it. I did Gleevec for life because of the trial.
Andrew Schorr:
Okay. Dr. Schilsky, let me just ask you, is that a benefit typically of trials? Like with these oral cancer medicines which you know can be so expensive, if you’re in a trial for one do you get it for life or an extended time or how does that work?
Dr. Schilsky:
Depends a little bit on the trial and the sponsor for the trial, but the one thing for sure is when you’re on a trial whatever the investigational drug is, whatever is being researched, that’s provided for free. And any testing that would be considered to be for research purposes is provided by free‑‑for free. So that’s a benefit of participating in the trial.
Typically the drugs continue to be provided for free for as long as the patient continues to benefit. Now, sometimes if the drug ultimately gets FDA approved then it may be necessary at some time in the future for a patient to switch over from the research drug to the commercial drug, but of course at that time the drug is FDA approved and if the person has insurance it will generally be covered by their insurance.
Andrew Schorr:
Okay. We got a question in though for you, Dr. Schilsky, from Darrell. We were talking about genomic testing to understand what version of a disease we have either because of our ethnic background or some other thing that’s going on with us. As you know, insurance companies for a while have been balking at some of these more sophisticated tests, yet we and our doctor need that for us to get what may be right on target for us. So maybe you could talk about work that ASCO’s doing at all related to that. We want the testing done, but we also want to get it paid for so we can get that right, precise care.
Dr. Schilsky:
Yeah. It’s a complicated question because the testing is done at different points in the person’s illness. And so typically a test on a tumor specimen that’s necessary to determine a standard of care treatment, and many of these tests are referred to as companion diagnostic tests. Those tests typically are covered by insurance because the treatments themselves are also covered by insurance and the only way to know if you can get the treatment is to have the test done.
Now, where it gets a little bit uncertain is when you get into this sort of large‑scale genomic testing where a patient’s tumor might be tested for many hundreds of genes not really knowing what you’re looking for and not really knowing what you’re going to do when you find it. And that is where you’re beginning to bump up a little bit against, research and that’s where the insurance companies, sometimes some are reluctant to pay for that kind of testing.
Now, at least one of those large genomic profiling tests earlier this year was approved by both the FDA and Medicare and now will be reimbursed. So that’s the good news, and I think that’s the direction that most insurance companies are heading in.
One of the things that my organization is doing to try to understand how best to use these tests and how best to use targeted cancer drugs is we’re doing our own clinical trial that’s available in 20 states around the country, so not the entire country yet, but has already enrolled more than 1200 people on the study over the last two and a half years. And we’re doing this study to understand how this kind of genomic testing is done, what kind of treatment is recommended based on the results of the genomic test and whether or not that treatment actually works.
Andrew Schorr:
Cecelia, you mentioned earlier about the lady walked into the health fair and when you started talking to her about trials she said I got to go to work, and she walked out. And Dr. Schilsky was talking about eligibility requirements, but there are other issues where the study may be asking you to come back to some place or have multiple tests with some frequency so it’s not just leaving work one time. It may be leaving work 20 times. Have you had people voice that concern to you, that it’s just‑‑what’s being requested is just too much?
Cecelia Mann:
Yes. I think the lack of convenience for people who don’t have the funds or don’t search out the funds would definitely hinder them being on a clinical trial or being open to hear about the clinical trial. So, yeah, convenience and awareness. We try to spread awareness that, yes, after we talk about the disease, the myeloma and the symptoms then we go into the resources. And, you know, I make sure I tell them about calling the information line and talking to the masters level oncologist professional there and finding out about the latest trials, the latest treatments in addition to what they’re doing currently with their doctors or their family members or friend that is diagnosed with one of the blood cancers.
Andrew Schorr:
Dr. Schilsky, she’s getting at helping people sort out what trials are available. So medical science is a moving forward, and I’m sure you as an oncologist say, hallelujah, there are more trials than ever, but it’s often not only daunting to understand any one of them but to go through a bunch of them to understand what might be right for you. So how can ASCO help that? Is it just simply educating your doctor, or what can we do for families affected by cancer so they can get at what could be a match for them?
Dr. Schilsky:
Yeah, it’s a great question. So there are a lot of resources available, as Cecelia has mentioned. We can help patients understand and even begin to sort of, you know, wade through and winnow down the potential clinical trial options for them. One things that we’re working on and very interested in doing is sort of flipping the current paradigm by which trials are done. So right now, typically speaking, the patient has to travel to whatever site has the trial available. If they’re fortunate enough that that’s their own doctor’s office, that’s great, but, as in Mel’s case he had to travel to MD Anderson to get the trial.
The technology these days is at a point where we think we can flip that. Instead of making the patient go to the trial we’re going to work toward making the trial come to the patient. So if your doctor is aware that a trial exists somewhere in the world it should be possible for the doctor to basically just go to a website, find the research study, find the consent form, find the other documents that are necessary and present that to the patient. And if the patient qualifies just sign them up instead of making the patient travel hundreds of miles away to the one place that has the trial available.
Some trials have already gone down this road, and they’ve actually been recruiting very successfully, but it’s still not the usual way in which things are done, and we think we need to try to flip things around a little bit to make it easier for the trial to come to the patients. Let the trial travel. Let’s not make the patient travel.
Andrew Schorr:
That sounds great.
Mel Mann:
Can I add something to that, Andrew?
Andrew Schorr:
Sure.
Mel Mann:
Okay. As a veteran, I was part of the VA system, and I had to go out to MD Anderson, but this summer they started something called Navigate, the VA had started something called Navigate, which partners with the NCI. And it’s at 12 sites around the country, and it’s to bring the clinical trials to the VA. It’s right there. So if it’s an NCI clinical trial then the veteran can get on that clinical trial. And there’s a lot of African‑American veterans who can take advantage of that.
Andrew Schorr:
For sure. That’s terrific. So we’re going in the right direction. One other thing I think that needs to change is we talked about the scientists, whether they’re federal government scientists or drug company scientists, and they want to get answers to a whole bunch of scientific questions. So they may say, as you write the protocol I think it is, well, you have to get so many CT scans and you have to get so many blood tests and stuff like that. And it can become onerous, Dr. Schilsky.
What’s happening in trial design so that, A, we talked about eligibility, you can get into the trial, but the things you’re asking of me may have logistical hurdles as well that you’re kind the lightening up on it to get to the key scientific question without all these other bells and whistles that make it tough on me.
Dr. Schilsky:
Yes. I like to think of it as the need to know and the nice to know, right? There are certain things you need to know in the trial to be sure that the treatment is working, the patient is safe and not having any severe side effects and things of that sort. A lot of that stuff is the same stuff that doctors order every day on their patients as part of routine clinical care, and so much of what needs to be collected in clinical trials really aligns pretty well with standard of care.
Now, that said, because clinical trials are research and because there’s always new frontiers to explore, sometimes testing in a clinical trial extends beyond what the standard of care is. Sometimes patients are asked to give extra specimens of their blood, of their normal tissues, of their tumor tissues. Extra biopsies might be required, things of that sort. Patients need to understand why they’re being asked to do that, what those specimens are going to be used for, how is it going to advance research.
And, frankly, they’re very important to expanding the scope of the research. So, for example, oftentimes those specimens are used. If the treatment doesn’t work in a patient having those specimens can help the scientists understand why the treatment didn’t work, and that opens up a whole new horizon to explore to potentially make the treatment better in other patients.
Andrew Schorr:
Mel, do you recognize that by being in a trial and the work that you and Cecelia have been doing that you’ve probably helped thousands of patients by first being in a trial and then you and Cecelia talking about it?
Mel Mann:
Yeah. Yeah. I guess that’s kind of hard sometimes. You don’t see yourself in that role, but as I look back on it, yes.
Andrew Schorr:
Cecelia, you’ve probably talked to a lot of people. Have you seen a change where‑‑you’ve been doing this for a number of years where earlier on people said no, no, no. Are people more receptive? Do you see a change going on? Let’s say in the African‑American community, do you think people are a little more receptive?
Cecelia Mann:
Yes, I think so. I think they are more receptive, and this has a lot to do with education and awareness, and that’s what we are out there doing when we are out there in the community. And the more they hear about it and the more they read about it and the more they can see examples like Melvin, and we know one or two other people that we’ve met that were also on a clinical trial. One is in our church, and he had a type of leukemia, and we didn’t know why he was sick. But he is doing very well.
And so the more we can get those examples out there in the community of successful clinical trial patients, it really helps and goes a long way toward helping people of color relax and come aboard. And I just say, please, do your research, educate yourself and ask questions and please stay open and don’t dismiss clinical trials out of hand.
Dr. Schilsky:
And, Andrew, if I could just add to that. I just want to make the point that it’s people like Mel who are creating the future. Everything we know about how to treat cancer we learned from the people who participated in the clinical trials. We’ve been doing clinical trials in cancer for at least 70 years, and all of the standard of care treatments that we have today came from the participation of people in clinical trials. And that’s how we make progress. That’s how we’ll continue to make progress.
So it’s the clinical trial participants who, sure, they’re in it for themselves. We understand that. They’re looking for a new treatment, a better outcome, but they are the heroes of oncology because they are paving the way, trying the course and ultimately making a better future for every cancer patient who follows them.
Andrew Schorr:
Amen. Let me just recap a couple of things, and correct me if I get anything wrong, either of you. So, first of all, Dr. Schilsky, I know there are more trials now than ever before, and they’re now looking at these rare subtypes as well, and so if we participate we may get the benefit of tomorrow’s benefit today. Cecelia was talking about assistance programs, people to help you sort it out, that you are noticing how there are difference among us about the ways that drugs are effective or not, and that’s so important to learn.
If we partner with you, Dr. Schilsky, and the many thousands of oncologists and researchers that you represent, can we get to the goal line faster? In other words, are you hopeful that if we really consider trials and participate in trials and stay in trials and the different groups that we can get closer to cancer cures?
Dr. Schilsky:
Absolutely. I mean, we have more and better cancer treatments today than we’ve ever had before. We have all sorts of new and hopeful treatments on the horizon. We have to prove that they are safe and effective treatments to get them out there into routine clinical practice, and that’s where the clinical trials come in. So the more people who participate in trials the more quickly those trials can be completed and give us an answer, then the more quickly those drugs will make their way into standard clinical practice where everybody can benefit from them.
Andrew Schorr:
Okay. So a couple of to‑dos for our audience if you’re a patient or a loved one or however you hear this. Ask your doctor about whether trials apply to you or your loved one who is diagnosed with cancer even if it’s on day one. You don’t have to be at death’s door. You’ve been diagnosed or a diagnosis is suspected, what tests can we do, how do we know what we’re dealing with, and when we look at the treatment options is a trial a possibility if that makes sense, right?
Dr. Schilsky:
Absolutely.
Andrew Schorr:
Okay. Step two, are there resources to help me overcome any obstacles I may have to participation, first understanding the trial, understanding it in my first language, sorting out is it right for me, getting to where it is and then staying in the trial because many people, unfortunately, don’t stay in the trial and so how do be help the trial get to the goal line?
And then lastly, Dr. Schilsky, it sounds like you’re doing a lot at the community level to have more doctors have an easier time of the bureaucracy that we’ve had with trials before and the understanding of this flood of trials that’s happening, right?
Dr. Schilsky:
Absolutely. And, you know, to be perfectly honest, the clinical trial community has‑‑we ourselves have created some of the bureaucracy, some of the excess regulation, some of the barriers to participation. It’s up to us to strip those away and solve the problem and make clinical trials more broadly available. We are working very hard now to make that happen.
Andrew Schorr:
Okay. So whatever community you’re in. I’m in the Ashkenazic Jewish community. Mel and Cecelia are in the African‑American community. We have people watching who are in the Hispanic community, the Asian community. If you have benefited from a trial, talk it up, right? Cecelia, people should talk it up, correct?
Cecelia Mann:
Exactly, yes. Please, talk it up.
Mel Mann:
Yes.
Andrew Schorr:
Mel, thank you. I wish you really continued good health. How many years has it been since you were diagnosed?
Mel Mann:
Well, in about two months it will be 24 years.
Andrew Schorr:
Twenty‑four years, and for me it’s 22 years. And had there not been trials either that we were in or somebody else was in we wouldn’t be here.
Mel Mann:
Yes.
Andrew Schorr:
So, thank you. And also, Cecelia, thank you for being a community activist when it comes to trials and being supportive of Mel as he’s been in a trial because some other people would say, you can’t go there, you can’t do this, and you’ve been supportive every step of the way. Thank you for that.
Cecelia Mann:
Oh, you’re so welcome. It was a pleasure to do it.
Andrew Schorr:
Mel and Cecelia Mann from Atlanta. And Dr. Richard Schilsky, you’ve devoted your life to this, Dr. Schilsky, and I just want to say on behalf of the cancer patient community thank you and thank you for the leadership that ASCO is trying to do, both with changing research requirements, working with government, working with industry, and you thank you personally for your devotion to us. I really appreciate you being with us.
Dr. Schilsky:
It was my great pleasure. And, again, congratulations to Mel and Cecelia.
Andrew Schorr:
Okay. Thank you all. So this is what we do with our Clinical Trials Mythbusters program. Please tell others about it. The replay is available very shortly and all kinds of little highlights that we’ve done today. But what’s important is wherever you are is remember we can’t develop new medicines unless all of us work together to participate to get the scientific answers that apply to us, whatever our unique situation is, and then we can work with government to approve new medicines, get them on the market and so many people can benefit in the US and worldwide.
Thank you so much for being with us on this Patient Empowerment Network program. I’m gratified to be part of it. Thanks too to our financial supporters AbbVie, Astellas, Celgene and Novartis and their dedication to drug development and supporting and sponsoring clinical trials. I’m Andrew Schorr near San Diego. Remember, knowledge can be the best medicine of all.
Please remember the opinions expressed on Patient Empowerment Network (PEN) are not necessarily the views of our sponsors, contributors, partners or PEN. Our discussions are not a substitute for seeking medical advice or care from your own doctor. That’s how you’ll get care that’s most appropriate for you.






 Each company has a different process for enrolling in its PAP. Some applications require extensive financial information, while others require basic information; Some require doctors to fill out a portion of the application, while others only need a signed prescription. Miller says for the Genentech enrollment process, he had to provide his financial information and that the application had two or three pages for his doctor to fill out. Rosenguard says the Celgene application process was extremely simple and that it took about two weeks for him to be accepted into the program.
Each company has a different process for enrolling in its PAP. Some applications require extensive financial information, while others require basic information; Some require doctors to fill out a portion of the application, while others only need a signed prescription. Miller says for the Genentech enrollment process, he had to provide his financial information and that the application had two or three pages for his doctor to fill out. Rosenguard says the Celgene application process was extremely simple and that it took about two weeks for him to be accepted into the program. PAP Basics
PAP Basics