What Do You Need to Know When Considering CAR T-Cell Therapy?
What Do You Need to Know When Considering CAR T-Cell Therapy? from Patient Empowerment Network on Vimeo.
How does one access myeloma CAR T-cell therapy? This animated explainer video provides an overview of the steps involved in determining whether a patient qualifies to receive CAR T-cell therapy, what the process entails, common side effects, and why having a care partner is essential.
See More From Thrive CAR T-Cell Therapy
Related Resources:

Understanding CAR T-Cell Therapy | How It Works and Who It’s Right For |

|

|
Transcript:
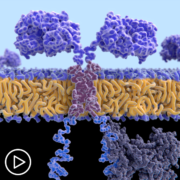
The emergence of CAR T-cell therapy is revolutionizing treatment for some people with myeloma. But, who is it right for, and what is the process for people that qualify?
- The first step in accessing this treatment is to be referred by your physician to a center that specializes in CAR T-cell therapy.
- Then, a consultation will take place with the transplant team, and a health assessment is administered to ensure patients are healthy enough for CAR T-cell therapy. This includes testing to review the current status of your cancer and testing of your body’s major organ systems.
- Next, the specialty center will evaluate the best type of CAR T-cell therapy for the patient, including clinical trial options.
- After approval, financial coordinators will discuss insurance and therapy costs with the potential recipient. Logistics are also arranged at this time, which may include help with transportation and housing, if necessary.
- Medical centers also require that patients have a care partner, such as a family member or friend, who can be with them at all times, particularly after leaving the hospital.
So, what is the process once a patient is approved for CAR T-cell therapy? Once a patient is approved to move forward with the procedure, a date is set for collection of the patient’s T cells. T-cells are collected during a process called apheresis. During apheresis a specialized machine filters the patient’s blood to remove the T-cells for collection and the rest of the blood is returned to the patient.
After collection, the T cells are sent for manufacturing. During that time, the patient is given a “bridging therapy” to maintain the myeloma until the CAR T cells are infused.
Once the CAR T cells are infused, the patient will be closely monitored by the CAR T center. This may or may not include hospitalization depending on the policies of the treatment center. Patients and their care partner should plan to stay close by the center for up to 30 days after the infusion.
During this time, the patient is evaluated for their response to treatment and monitored for possible side effects so that they can be managed in a timely manner.
The potential side effects of CAR T-cell therapy may include:
- Cytokine release syndrome, or CRS, which is an aggressive response to treatment by the immune system and may cause symptoms such as low blood pressure, high heart rate decreased oxygen saturation, fever, nausea, and body aches.
- Another possible side effect is neurotoxicity, which is an adverse event that may cause issues such as confusion, difficulty with communication, seizure, or tremors.
- And, another side effect may be low blood counts, which could impact the immune system and increase risk for infection.
Every patient is different, so close monitoring is essential.
So now that you know more about CAR T-cell therapy, you can work with your healthcare team to decide if this treatment option may be right for you. Be sure to speak up and ask questions. Remember, you have a voice in YOUR myeloma care.
To learn more about myeloma and to access tools for self-advocacy, visit powerfulpatients.org/myeloma.