What Is MRD-Positive Acute Myeloid Leukemia?
What Is MRD-Positive Acute Myeloid Leukemia? from Patient Empowerment Network on Vimeo.
What do acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients need to know about MRD-positive AML? Dr. Catherine Lai from Penn Medicine discusses minimal residual disease (MRD). Learn about the meaning of MRD, complete remission, and MRD testing methods.
[ACT]IVATION TIP from Dr. Lai: “Ask if MRD testing can be done on your bone marrow biopsy at the time at which you or after you’ve had your chemotherapy.”
Download Resource Guide en español
Related Resources:

What AML Treatment Options Are Available for MRD-Positive Patients? |

|

AML Clinical Trials Critical to Treatment Breakthroughs and Improvements |
Transcript:
Art:
Dr. Lai, what is MRD-positive AML?
Dr. Catherine Lai:
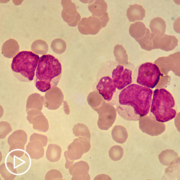
So, that’s a really good question. And to answer that question, I’m going to actually answer a different question, which is, What is the definition of complete remission? So the definition of complete remission is when we do a bone marrow biopsy, and we have less than 5 percent of those blasts or leukemia cells in the bone marrow, and that is also in the setting of a relatively normal immune system or normal other blood counts have improved, so that your neutrophil count is above 1,000, and your platelet count is above 100,000. So, MRD, which stands for measurable residual disease, means that you’re in complete remission, so you have less than 5 percent blasts, but you’re more than zero.
And we, in general, when patients who are MRD-positive, we know that if you were to do nothing, that those patients have a high likelihood of relapse. We know for the patients who are going to transplant, if you’re MRD-positive before transplant, those patients also have a higher likelihood of relapsing after transplant. And so we tend to monitor it if possible…the tricky thing is, is that there is not a standard way to measure MRD testing as of yet, the common approaches are right now are with either flow cytometry or with PCR or next-generation sequencing, if you have a particular targeted mutation that we can follow.
So your activation from that standpoint is to ask if MRD testing can be done on your bone marrow biopsy at the time at which you or after you’ve had your chemotherapy.