[ACT]IVATED: Empowering Endometrial Cancer Awareness & Action
Patient Empowerment Network (PEN) is committed to helping educate and empower patients and care partners in the endometrial cancer community. Endometrial cancer treatment options are ever-evolving with new treatments, and it’s important for patients and families to educate themselves about clinical trials, risk factors, barriers to and disparities in care. With this goal in mind, PEN continues to build on to its [ACT]IVATED Endometrial Cancer program, which aims to inform, empower, and engage patients to stay updated about the latest in endometrial cancer care.
Endometrial cancer awareness needs more visibility for multiple reasons. The incidence rate and mortality rate for endometrial cancer is increasing rather than decreasing, and the rates are rising more rapidly in non-white patient groups and ethnicities.
PEN is proud to add information about endometrial cancer to educate more patients and their families about this rising health concern. Cancer survivor Lisa Hatfield interviewed expert Dr. Charlotte Gamble from MedStar Health and Dr. Emily Hinchcliff from Northwestern Medicine as part of [ACT]IVATED Endometrial Cancer.
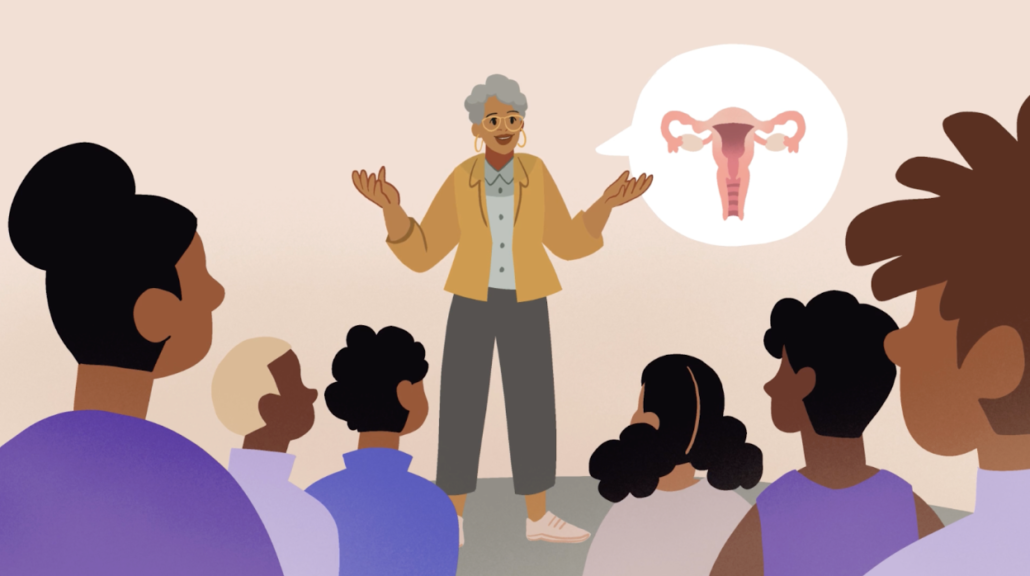

Endometrial cancer patient Sharon also shared her personal journey with cancer and highlighted some things she has learned. “After my cancer experience, I want to educate other women about what I’ve learned about endometrial cancer. Black women have nearly twice the death rate from endometrial cancer compared to white women. Hispanic, Black, and Asian women are not represented in clinical trials at equal rates to white women. And Black women are also diagnosed more frequently with rare but aggressive endometrial cancer forms.”
Endometrial Cancer Risk Factors
Endometrial cancer may result from one or more risk factors, so it’s vital for patients to educate themselves about risk factors for early detection and treatment. Dr. Emily Hinchcliff from Northwestern Medicine discussed known risk factors for endometrial cancer. “I… think the important ones to highlight are certainly obesity. This I think is a large driver of why there is increasing incidence of endometrial cancer. This relates to kind of the hormonal regulation. Obesity results in increasing levels of estrogen that disproportionately affect the endometrium. And then similar to that, certain hormonal syndromes where women have irregular or infrequent periods like polycystic ovarian syndrome can also put them at higher risk. More globally, I think age, family history are also risk factors. And then as I mentioned, unfortunately, women who are non-white have a higher risk of endometrial cancer mortality, especially as relates to some of the higher risk endometrial cancer subtypes.”
Some patients may have questions about the endometrial cancer risk of using hair straightening beauty products. Dr. Charlotte Gamble from MedStar Health discussed what is known and what still needs more research about this potential risk factor. “…within the past few years, there have been a few major studies that have looked at patients, looking back at patients who have then developed endometrial cancer and seeing what kind of risk factors they might have had compared to patients who didn’t develop endometrial cancers. And looking at the types of patients within these studies, there are some subtle differences that need to be addressed.
Dr. Gamble explained about the patient group in the research study. “One of the major studies was done in a cohort group of patients who had actually close family members who had breast cancer. And so this is actually a very specific type of patient population where they were already at somewhat of an increased risk of developing a type of a cancer, because they had a relative that had breast cancer. And in this cohort of patients, they found that the frequent use of hair straightener products was associated with a higher likelihood of developing uterine cancer.” The patient group was not only comprised mainly of patients with a relative with cancer but also mostly white patients rather than Black patients who most commonly use hair straightener products. With these major study issues that need additional research studies to resolve, there may be an endometrial cancer risk with the products, but no concrete conclusions can be drawn yet.

Endometrial Cancer Disparities and Challenges
At the National Institutes of Health (NIH), endometrial cancer is one of the lowest funded studies. Dr. Gamble discussed some of the encouraging news about endometrial cancer treatments. “…having major trials come out over the past couple of years that really look at survival opportunities with the leveraged use of immunotherapies is something that is both exciting and invigorating to the field and hopefully can potentiate further funding from the NCI to be able to study this disease type.”
Endometrial cancer is a cancer that shows some disparities in health outcomes. Dr. Hinchcliff discussed racial disparities and how research can help address disparities. “We know, as a field, as a kind of medical subspecialty, that there is a racial disparity in endometrial cancer mortality. While there is a lot of research going on to address the kind of potential biologic component there, is there something different about the cancers that are developed in different racial groups? I think there’s also really important research going on about the kind of systemic and cultural barriers and differences that women of different races experience that also can dramatically impact their cancer care.”
Clinical trials are the primary way to move research and treatment advancements forward for endometrial cancer patients. Dr. Gamble discussed primary reasons for clinical trial challenges. “A lot of times when we see that these trials that are published might not represent a racially diverse group of patients. Oftentimes it’s because of two reasons. One, patients aren’t even offered clinical trials, even if they are eligible. Or two, patients might be getting care at a health facility that doesn’t have access or the infrastructure to enroll them on these clinical trials that could be available, perhaps at a regionally nearby cancer center.”
Where patients live also has an impact on their health outcomes. Dr. Gamble shared information about patients residing in rural areas. “And it looks like patients who are living rurally don’t live as long as patients who live in the cities. And so just finding differences and seeing kind of how, again, this critical race practice and how the systems and structures in the United States have contributed or might contribute to these differences that we’re seeing, has classically and historically been easy low hanging fruit.”

Endometrial Cancer Care Solutions and Successes
With endometrial cancer disparities gaining increased awareness, researchers and healthcare systems have undertaken some efforts to reduce disparities in health outcomes. Diagnostic testing tools and clinical trial support are two ways to help improve endometrial cancer care in underrepresented communities. Dr. Hinchcliff discussed undertakings by Northwestern University. “So one of the ones that I have been working on closely is there is an ever-increasing number of diagnostic testing tools that we have within our kind of armamentarium. And so one particular test that patients may have read about or heard about is something called circulating tumor DNA.” Dr. Hinchclliff continued about efforts to improve clinical trial access, “The other thing that one of my colleagues here is working on is trying to really create access for women who have limited access to healthcare. So we have developed a clinical trial platform to allow the women, specifically of Chicago, to better understand their options for clinical trials across the institutions in Chicago.”
[ACT]IVATED Endometrial Cancer Program Resources
The [ACT]IVATED Endometrial Cancer program series takes a three-part approach to inform, empower, and engage both the overall endometrial cancer community and endometrial cancer patient groups who experience health disparities. The series includes the following resources:
- [ACT]IVATED Expert Interviews
- [ACT]IVATED Patient Vignette
- [ACT]IVATED Toolkit
- [ACT]IVATED Resources
Though there are endometrial cancer disparities, patients and care partners can be proactive in educating themselves to help work toward optimal care. We hope you can take advantage of these valuable resources to aid in your endometrial cancer care for yourself or for your loved one.





![SCLC [ACT]IVATED](https://powerfulpatients.org/wp-content/uploads/Screenshot-2024-01-09-at-1.22.18-PM-1030x584.png)

![SCLC [ACT]IVATED](https://powerfulpatients.org/wp-content/uploads/Screenshot-2024-01-09-at-1.25.27-PM.png)

![Dr. Shah's [ACT]IVATION Tip](https://powerfulpatients.org/wp-content/uploads/Screenshot-2023-08-14-at-10.37.31-AM-1030x550.png)

![RMC [ACT]IVATED Tip](https://powerfulpatients.org/wp-content/uploads/Screenshot-2023-06-21-at-11.20.10-AM-1030x550.png)
![RMC [ACT]IVATED Tip 2](https://powerfulpatients.org/wp-content/uploads/Screenshot-2023-06-21-at-11.21.35-AM-1030x578.png)
![RMC [ACT]IVATED Tip 3](https://powerfulpatients.org/wp-content/uploads/Screenshot-2023-06-21-at-11.22.56-AM-1030x586.png)


