The term “patient empowerment” is among the top buzzwords in health care circles, but as with many buzzwords, they can mean different things to different people. The term is most often used to emphasize the value of having patients assert greater control over their health and health care. WHO defines empowerment as “a process through which people gain greater control over decisions and actions affecting their health” (WHO 1998). This shift is due in large part to the use of technology that facilitates increased patient access to information via the Internet, peer-to-peer sharing, consumer health devices, and mobile apps.
In a recent Twitter chat, I set out to explore what it means to be an empowered patient today. The global participation of those who shared their views on the topic shows that patient empowerment is something of universal interest.
Seven Essential Components of Patient Empowerment
1. Information
Information is fundamental to the process of patient empowerment. Rare disease advocate and parent, Anne Lawlor (@22Q11_Ireland) believes that “an informed educated parent is an empowered one.” Patients make the best decisions when armed with the right information. To make genuinely informed decisions about our treatment we must have access to the relevant information needed to make those decisions. “Being informed is key to empowerment for me,” says specialist palliative care social worker, Deirdre McKenna (@KennaDeirdre). “Accurate information, clearly communicated and an available space to discuss and explore options and choices.”
Research shows that access to the right information, at the right time, delivered in the right way, leads to an increase in a patient’s desire and ability to take a more active role in decision-making. Open and transparent communication and access to a patient’s own medical records is a key driver of patient empowerment. Medical Director and Consultant Surgeon, Dermot O’Riordan (@dermotor) believes to truly empower patients “we should be aiming for the “Open Notes” principles of default sharing of all documents.” As patient advocate and CEO of Medistori Personal Health Record, Olive O’Connor (@MediStori) points out, “the patient is at the very core of every single service they use – they know everything there is to know about themselves, in the home and outside of it. Yet patient records are not kept with them!”
The OpenNotes initiative began in 2010 as a year-long demonstration project, with 105 primary care physicians at three diverse U.S. health care centers inviting 20,000 patients to read visit notes online through patient portals. Findings from the study suggest that shared notes may improve communication, safety, and patient-doctor relationships, and may help patients become more actively involved with their health and health care. Evidence also shows a sixty percent improvement in the patient’s ability to adhere to medications, a major problem with managing chronic pain conditions. What is key to the discussion on patient empowerment is that this initiative “demonstrates how a simple intervention can have an enormous impact, even absent advanced technology” (my emphasis).
2. Health Literacy
While access to information is a key driver of patient information, health literacy is defined as “the degree to which individuals have the capacity to obtain, process, and understand basic health information and services needed to make appropriate health decisions.” (National Library of Medicine). Health literacy should come before digital literacy. “Health literacy is crucial,” says healthcare analyst, Matthew Loxton (@mloxton), “and you cannot get empowerment without health literacy.” Soo Hun (@soo_cchsc), Programme Manager at the Centre for Connected Health and Social Care, believes “digital is a key aspect but health literacy, even basic literacy is a must. Not all things digital requires tech know-how but all health information requires basic literacy. An app for meds reminder is no use if a patient lacks understanding of why medication is needed in the first place or why they need to be taken promptly. We spend too little time transferring knowledge to patients.”
This transfer of knowledge is crucial to the empowerment process, according to Olive O’Connor. “At the first point of contact with the patient,” she says, “education on how, what, why, where and when in relation to a condition or medication should be talked through fully. All other tools (digital, leaflets etc.) should come after the conversation which is key to empowerment.”
3. Digital Literacy
Cornell University defines digital literacy as “the ability to find, evaluate, utilize, share, and create content using information technologies and the Internet.” It’s interesting to note that opinions vary on whether digital literacy is essential to patient empowerment. RN turned patient advocate and health activist, Kayoko Ky Corbet (@kkcorbet) doesn’t believe that “digital literacy is an absolute requirement, but the ability to find accurate relevant information, and understand the information is.” Breast cancer advocate, Jennifer (@vitalfrequencis) agrees that “digital literacy is not fundamental and should not be part of the equation. Empowerment needs to be across all socioeconomic groups. Otherwise…a whole bunch of patients may never be empowered.”
Dermot O’Riordan is convinced that “whilst it sounds nice to say that digital is not ‘necessary’ for patient empowerment, in practice it is going to be pretty tough to do it properly/completely without digital.” Transplant recipient and rare disease patient, Carol McCullough (@Imonlyslightly ) also believes “digital literacy strengthens the empowerment process.” She too points to “access to your medical information online” as a key component of the empowerment process. “Knowing your personal medical data is strength, as is education about your illness,” she says.
Maternity campaigner, SeánaTalbot (@SeanaTalbot) believes that “those with long-term conditions and access to technology have a better chance of accessing information and support.” Indeed many patients have found in the online world of peer-to-peer healthcare an environment in which they are supported to become a more empowered participant in their healthcare. As I look back on my own empowerment journey, my progress was advanced step-by-step by learning more about my disease initially from doctors, then through Internet searches, and most helpful of all through patient peers online. Finding and being part of a patient community can be an important step on the path to empowerment.
4. Self-Efficacy
Self-efficacy, as it relates to healthcare, is belief in your ability to effect change in outcomes so that you can achieve your personal health goals. The patient empowerment definition which comes to us from the European Patient Forum describes empowerment as a process that “helps people gain control over their own lives and increases their capacity to act on issues that they themselves define as important.”
Developing a sense of personal control over your health is in itself empowering. The empowered patient is confident in their ability to manage their condition. When unsure about where to go or what to do next they will feel confident to ask questions of the healthcare professionals providing their care. This confidence comes easier to some than others, and even the most confident may need guidance from their doctors in managing their disease. Endocrinologist, Iris Thiele Isip Tan, MD (@endocrine_witch) points out that “some of my patients are surprised when I teach them how to adjust/titrate insulin doses. Apparently not all MDs ‘allow’ this. Some need handholding because they get anxious about the responsibility.”
Digital leader and physiotherapist, Linda Vernon (@VernonLinda), believes “for authentic patient engagement to occur, we need to establish what the patient brings to the table, something akin to an individual, personal take on Asset-Based Community Development – perhaps we could think of it as Asset-Based Personal Development, supporting the patient to tap into their own internal, community or environmental resources to improve their health and wellbeing. Engaging patients should be as much about exploring what they can do for themselves and to help the health and care system, as what we professionals can offer to the patient.”
5. Mutual Respect
The healthcare professional is the most important contact point for the patient and the system and (dis)empowerment often manifests in the patient/professional relationship. At the heart of the empowerment approach is seeing the patient-professional relationship as a partnership of equals. Carol McCullough describes it as a reciprocal process of “mutual respect for what each person knows and being allowed to make informed choices. It is not about command and control.”
This is a partnership approach that seeks to balance clinician expertise with patient preference. It recognizes that while healthcare professionals are the experts in their knowledge of a disease, patients are the experts by experience. The empowerment process is about sharing both knowledge and experience to set new goals and learn with and from each other. Dr Kit Byatt (@Laconic_doc) agrees. “Many patients are experts”, he says, “especially rare disease patients. I’ve learned from many in my career.”
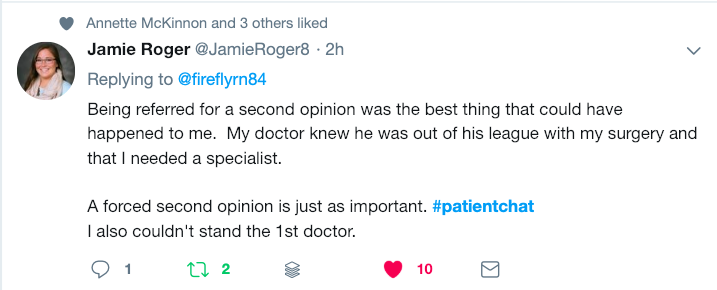
Building better relationships and seeing the patient as more than ‘just a patient’ was a recurring theme in the Twitter chat. Elena Vaughan (@StigmaStudyIE), who is researching the impact of HIV-related stigma in Ireland, believes that “an empowered patient is treated with respect, involved in shared decision-making regrading care and treatment, and is not patronised. For people with chronic conditions, effective communication, continuity of care and establishing a relationship of trust is very important.” Sometimes, as ME blogger and patient advocate, Sally Burch (@KeelaToo) points out, “not all patients are lacking confidence to speak. The problem is being heard.”
Patient and community advocate, Triona Murphy (@Murpht01) advises doctors to get to know your patients as individuals. “Know your patient!!…and their family,” she says. “No one size fits all! BUT there was/is still a culture of the ‘person’ stops at the door of the hospital and that person is now a patient.’” As antibiotic resistance campaigner, Vanessa Carter (@_FaceSA) says, “I might be a patient but I am also a creative director by profession. No one recognises me on that level. They see me as an underdog.”
6. Shared Decision Making
This partnership approach allows for Shared Decision-Making (SDM) – the conversation that happens between a patient and clinician to reach a healthcare choice together. Examples include decisions about surgery, medications, self-management, and screening and diagnostic tests. There is ample research which suggests that health outcomes are better in patients who are more involved in decisions about their treatment.
In the SDM model, the clinician provides current, evidence-based information about treatment options, describing their risks and benefits, and the patient expresses his or her preferences and values. Matthew Loxton points to how seldom we have metrics to track whether patient goals are being met. “Yet this,” he believes, “is THE most important part of quality.”
7. A Facilitating Environment
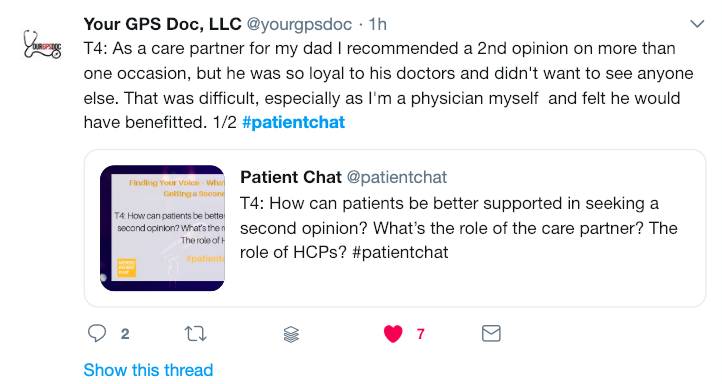
Linda Vernon defines patient engagement as “activating the person’s inner assets and supporting them to make the best use of them.” Being supported is a key component of patient empowerment. Many patients would like to take more responsibility for their own health and care, given the opportunities and support to do so. Empowerment does not happen in a vacuum: it is a two-way process. The patient needs a counterpart in the health professional who welcomes the patient’s involvement and knows how to create an enabling healthcare environment. Kayoko Ky Corbet states she became an independent patient advocate when she realized most doctors simply do not have the time (and often skills) to take this facilitating role and promote shared decision-making that patients desperately need. As Patient Critical Co-op (@PatientCritical) puts it, “if you have a patient who wants to advocate for themselves, and become informed, you also need a doctor that respects the patient’s right to share decision making.”
Is It Empowerment or Participation?
Not everyone likes to use the term “empowerment”, as it implies that it is an authority given to someone to do something. “I balk at the idea that professionals can ‘give’ (usually on their terms) power to the powerless,” says Alison Cameron (@allyc375). “We need to create conditions whereby people can “empower” themselves.” Seána Talbot agrees that patient empowerment “doesn’t mean ‘giving’ people power.’ Rather it’s about ‘enabling’ them to recognise and use their power.”
Perhaps the term ‘participation’ (which is a more active state) is preferable? This distinction is important because empowerment cannot be imposed ‘top down’ (although it can be facilitated). Sharon Thompson (@sharontwriter) believes that “patients should not be pressurised or need to be in a position of ‘power.’ It should be automatic that a patient is central and key to their care. Patients are automatically empowered when they are respected as being people who are entitled to understand and know about their care.”
Neither is patient empowerment about the patient taking full control or shifting responsibility to the patient. “If the empowerment amounts to abandonment”, says Matthew Loxton, “then the patient’s health goals are not being met. Patient empowerment should never be an excuse for abandoning or burdening the patient.”
Rather, the empowerment approach, as defined by the European Patient Foundation (EPF) “aims to realise the vision of patients as ‘co-producers’ of health and as integral actors in the health system.” Caregiver Reinhart Gauss (@ReinhartG) agrees that “patient advocates want to work with not against doctors – to share experiences and to grow in knowledge.” Vanessa Carter is clear that “we still want our doctors, but they are not there 24/7 so patients need the right tools to make self-care possible.”
Equally, it is about recognizing that there are degrees of involvement and not all patients wish to be ‘empowered.’ There is a spectrum of interest in wanting to assume an active role in care – from being passively receptive to fully engaged. It is up to the patients themselves to choose their own level of engagement. Pharmacist Chris Maguire (@chris_magz) sees this choice as the essence of empowerment. Patients “get to decide how much they want to look into things and take control. Or they want to be guided on the journey and have trust in their healthcare providers. But the key is that they decide the level of interaction and are not dictated to.” Kayoko Ky Corbet agrees that “true patient empowerment should be about helping patients get involved at their highest potential or at the level they choose.” However, she says “it’s also important to keep the option of involvement open. Ideally patients should get opportunities to change their minds to participate in decision-making later.”
Empowerment as an Ongoing Process
Empowerment is a non-binary, non-linear process. Your needs may change over time. You might feel empowered in a certain context, but disempowered in another. Healthcare communicator, Michi Endemann (@MichiEndemann) makes the distinction that “talking about empowerment as a healthy person is quite different than talking about it as a patient.” As patient advocate, Rachel Lynch (@rachelmlynch) puts it, “it can be quite tiring being empowered when all you want to be is well.” A sentiment echoed by Kathy Kastner (@KathyKastner), founder of Best Endings, who clarifies how “to me ‘empowered’ assumes I’m feeling physically and mentally up to the task of ‘being engaged’. I’ve seen powerhouses who cannot bring themselves to take responsibility for their own health.”
Mental health advocate and co-founder of #DepressionHurts, Norah (@TalentCoop) calls attention to the fragile nature of empowerment. “Even the strongest can quickly feel disempowered by a deterioration in health,” she says. “Fear disempowers. Sometimes it’s a case of ‘can’t’ not ‘won’t.’”
For those who feel ready for a greater degree of participation in their healthcare (and that of their family and loved ones), Jennifer advises that “being willing to self-advocate, along with self-confidence, communication skills, compromise, research skills, and relationship building” are some of the key traits and skills you need to become an empowered patient. Terri Coutee (@6state), patient advocate and founder of DiepCjourney Foundation, adds that “empowered patients do their research, ask questions, go to appointments organized, and take a friend to help listen.”
Barriers to Patient Empowerment and Overcoming Challenges
What are some of the current barriers to involving patients more in their care? Jennifer points to a “lack of adequate time during the doctor’s visit (on both sides), language barriers, technology barriers, generation gaps, and cultural gaps.” The solution? “All solved by building good relationships,” says Jennifer.
Norah also calls attention to the technology barriers. “For older patients simple things like communication (hearing), or uninformed changes are extremely disempowering; as is over reliance on technology for a generation who may not have ‘tech’ understanding or access.” Tim Delaney (@FrancosBruvva), Head of Pharmacy at a leading hospital in Ireland highlights the fact that “in acute hospitals we treat huge numbers of elderly people whose engagement with social media and new technology is lower. We need to design technology that meets their usability needs AND use whatever suits them best be it old tech or new.” Soo Hun agrees that “the tech savvy few have quicker and better access to health information and therefore can have choice and autonomy. To reverse that we need to make technology ubiquitous and make health information and choice easily accessible.”
Whilst Vanessa believes it should be “governmental policy to have digital resources in place, for example, disease specific websites / apps supported by health authorities,” Kayoko believes it can start with “tech-savvy advocates (like me) who could help patients learn to use simple digital tools.”
Matthew Loxton sees a core barrier to empowerment to be “the large knowledge/power gradients between patients and health care providers. Without access to their data, trustworthy sources of medical knowledge, and the power to execute their choices in achieving health goals, empowerment is an empty phrase.” Triona Murphy echoes this systemic challenge by clarifying that “the whole system needs to understand the patient’s right to be equal partners in their care. IF that is what the patient wants.”
Sometimes the fear of being labelled a difficult patient can be a barrier to empowerment. “Some patients feel uncomfortable challenging the judgement or actions of their caregivers for the fear of being labelled as ‘difficult’, of offending staff and/or because of concerns of compromising their healthcare and safety,” says Tim Delaney.
Final Thoughts
Not everyone wants to be empowered in making decisions about their care, and not every doctor wants to take the time. Some doctors use medical terminology which is incomprehensible to patients, while some patients have low health literacy skills or come from cultural backgrounds that lack a tradition of individuals making autonomous decisions. That said, Carol McCullough points out that while “not everyone may want to be empowered, for the health service to be sustainable, more people are going to have to take on more responsibility.”
Medical Doctor and Chair of Technical Advisory Board, Pavilion Health, Dr Mary Ethna Black (@DrMaryBlack) points to the inevitability of the shift towards patient empowerment. “Empowerment is an inevitable shift that is happening anyway, “she says. “We cannot turn back the tide or turn off the internet.”
Kayoko Ky Corbet agrees that we “must understand that patients making informed decisions is the ultimate way to reduce waste, pain and regrets in healthcare. It’s also morally the right thing to do!” Patient Critical Co-op also believes in the moral imperative that “empowerment essentially means a group or society recognizing your right. Patient empowerment exists as an action patients can take to improve themselves, but the key to achieving that improvement is having a group, organization, or state enshrine and recognize those rights.” In fact, the Alma Ata Declaration defined civic involvement in healthcare as both a right and a duty: “The people have the right and duty to participate individually and collectively in the planning and implementation of their healthcare.” The Declaration highlights the collective dimension of empowerment and the importance of action towards change. By working together to think internationally and act nationally we can draw on each other’s experiences so that as individuals and as a collective we can work towards better outcomes for all patients. To quote Terri Coutee, “When we gather our collective empowered voices, we feel a strong responsibility to give voice to others.”
I would like to acknowledge the assistance of Dr Liam Farrell in facilitating the Twitter discussion on which this article is based.
2020 Update: Patient Empowerment Revisited: What Does It Truly Mean To Patients?
To stay up to date on the latest cancer information and resources, sign up today!
A Stanford Medicine X e-Patient scholar, Marie Ennis O’Connor is an internationally recognized keynote speaker, writer, and consultant on global trends in patient engagement, digital health and participatory medicine. Marie’s work is informed by her passion for embedding the patient voice at the heart of healthcare values. She writes about the experience of transitioning from breast cancer patient to advocate on her award-winning blog Journeying Beyond Breast Cancer.










 Have you ever had the experience of leaving the doctor’s office wishing you had remembered to ask a certain question? Or have you left it until the very end to tell your doctor about the real reason for your visit? These so-called “doorknob” questions – bringing up an important concern just as you are leaving the office – can mean your doctor won’t have time to adequately address your concerns. When the average time it takes for a doctor’s visit is fifteen minutes, it’s easy to feel rushed and forget what you wanted to say, or to leave an appointment unsure of the information you have heard. But with a little advance preparation you can learn how to make the most of those fifteen minutes. Follow these fifteen tips to become a more empowered and engaged partner in your own health – and the health of those you care for.
Have you ever had the experience of leaving the doctor’s office wishing you had remembered to ask a certain question? Or have you left it until the very end to tell your doctor about the real reason for your visit? These so-called “doorknob” questions – bringing up an important concern just as you are leaving the office – can mean your doctor won’t have time to adequately address your concerns. When the average time it takes for a doctor’s visit is fifteen minutes, it’s easy to feel rushed and forget what you wanted to say, or to leave an appointment unsure of the information you have heard. But with a little advance preparation you can learn how to make the most of those fifteen minutes. Follow these fifteen tips to become a more empowered and engaged partner in your own health – and the health of those you care for.


